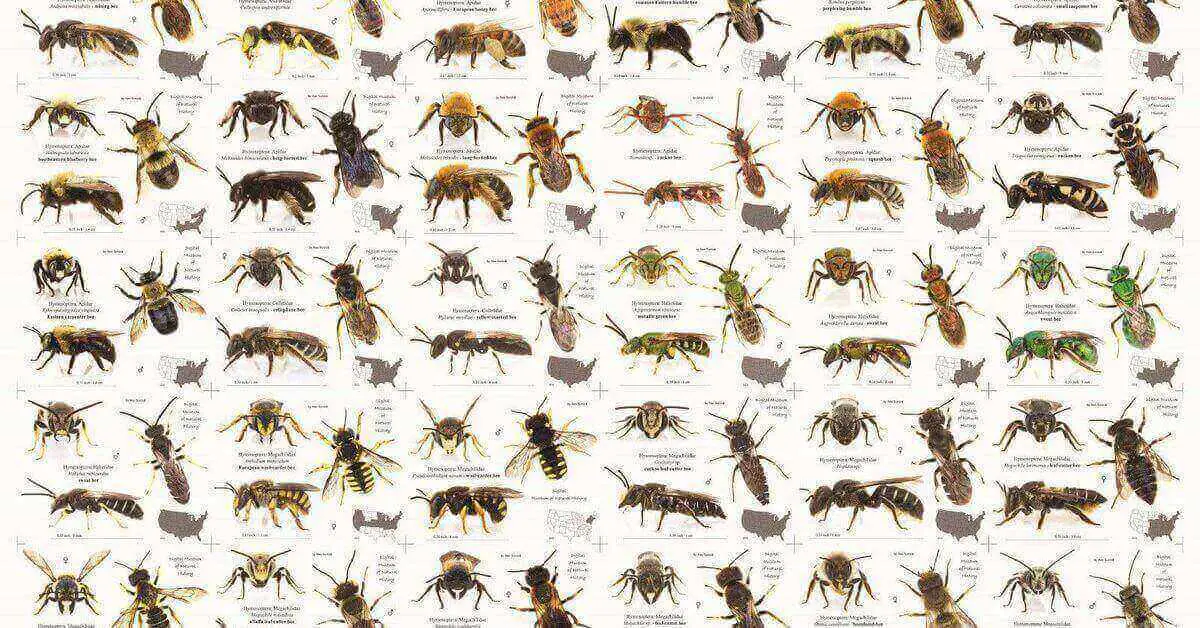
Ground nesting bees come in various species, each with unique characteristics. To effectively identify them, it’s important to observe their physical appearance and nesting behavior. Common ground nesting bee species include the Andrena, Halictus, and Colletes genera. These bees can vary in size, coloration, and markings, making them fascinating to study. In this artical we learn about Identification of Ground Nesting Bees.
Behavior and Characteristics of Ground Nesting Bees
Ground nesting bees are non-aggressive in nature, but certain circumstances can provoke defensive behavior. The males may become territorial, engaging in aggressive acts to protect their nests. It’s important to understand their behavior to avoid any potential conflicts. Ground nesting bees typically have a short lifespan, but they can establish new nests year after year.
The Importance of Ground Nesting Bees
Ground nesting bees play a vital role in pollination, ensuring the survival and propagation of many plant species. Their foraging activities contribute to the health and biodiversity of ecosystems. While their presence can be intimidating, it is crucial to appreciate their positive impact on the environment.
Are Ground Nesting Bees Dangerous?
Ground nesting bees are generally non-aggressive and pose little threat to humans. However, individual reactions to bee stings can vary, and some people may be more sensitive than others. If you or someone in your vicinity is allergic to bee stings, it is important to exercise caution and seek professional help when dealing with ground nesting bees.
Common Ground Nesting Bee Species
Ground nesting bees encompass a wide range of species. Understanding the different species can aid in identification and management efforts.

| Andrena bees | Which are often metallic black or dark brown |
| Halictus bees | Are known for their vibrant colors |
| Colletes bees | Are characterized by their fuzzy appearance |
List of bees that are known to live in the ground:
| Classification | Common Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Family | Andrenidae | Also known as mining bees, ground-nesting bees |
| Genus | Andrena | Includes many species of ground-nesting bees |
| Species | Andrena fulva | Tawny mining bee |
| Genus | Colletes | Includes species of solitary bees that nest in the ground |
| Species | Colletes inaequalis | Common eastern colletid |
| Order | Hymenoptera | Insect order that includes bees, wasps, and ants |
| Suborder | Apocrita | Suborder of Hymenoptera that includes bees and wasps |
| Superfamily | Apoidea | Superfamily that includes bees, including ground-nesting bees |
| Family | Halictidae | Sweat bees, including some ground-nesting species |
| Genus | Lasioglossum | Contains species of sweat bees that nest in the ground |
| Species | Lasioglossum zephyrum | Western s |
How to Get Rid of Ground Bees
If ground nesting bees have become a nuisance on your property, it’s essential to address the issue promptly and safely. Several control methods can be employed to manage their presence effectively. It’s crucial to choose a method that aligns with your preferences and the surrounding environment. Consider natural control methods and professional solutions to achieve the desired results.
- Nighttime Treatment
- Insecticidal Dust
- Soap and Water Solution
- Nematodes
- Nest Removal
- Prevention
Related Post’s
Natural Control Methods
For those seeking environmentally friendly options, natural control methods can help manage ground nesting bees. These include:
Modifying the habitat to make it less attractive to bees.
Applying targeted insecticides derived from natural ingredients.
Encouraging natural predators of ground nesting bees, such as birds and spiders.
Professional Control Solutions
If the ground nesting bee problem persists or poses a significant threat, it may be necessary to seek professional assistance. Pest control experts have the knowledge and tools to address the issue safely and effectively. They can assess the situation, recommend appropriate measures, and implement targeted control strategies.
Preventing Ground Bees from Returning
Preventing the return of ground bees requires a proactive approach. By implementing preventive measures, you can reduce the likelihood of future infestations. Some preventive steps include:
Modifying the landscape to discourage ground nesting.
Filling potential nesting sites with suitable materials.
Regularly monitoring and maintaining the property for early detection.
FAQ’S
Ground bees are generally non-aggressive but can exhibit defensive behavior if their nests are disturbed. It is important to approach their habitats with caution and avoid unnecessary disturbances.
Areas with sandy or well-drained soil attract ground bees, as these conditions favor nesting. Certain types of flowers and plants that provide ample food sources also attract them.
Ground bees typically have a relatively short lifespan, ranging from a few weeks to a couple of months, depending on the species and environmental factors.
Ground bees are not known for honey production. Unlike honeybees, which are social insects, ground bees are solitary and do not store honey.
Yes, ground bees are important pollinators. They play a significant role in the pollination of various plant species, contributing to the health and biodiversity of ecosyst
Conclusion
Identification of Ground Nesting Bees, though sometimes aggressive, are valuable contributors to the ecosystem as pollinators. By understanding their behavior and employing appropriate control methods, it is possible to coexist with these fascinating insects peacefully. Whether through natural or professional control solutions, it is essential to address any ground bee issues promptly and responsibly.